Home > Forest Woodlot > Forestry Work > Forest mapping Forest mapping
Buy: Forest mapping
Pictures of: Forest mapping
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Planfor
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Planfor
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Planfor
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Planfor
-
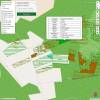
Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Copyright
-

Forest mapping
Author: Planfor
© Planfor
-

Forest mapping
2020 ETF* Certificate for Sustainable Forest Management - *Forest works company
Description: Forest mapping
I - What is Forest cartography?
II - How is a Forest cartography carried out?
III - Why create a forest cartography?
IV - Why carry out a cartography with PLANFOR?
I - What is Forest cartography?
The cartography of a forest is a graphic representation of cadastral and/or forest plots created from different data: administrative, fiscal, technical (tree varieties, ages, types…), geographical, soil conditions, trees mensuration, census by GPS, photography by plane, and others.
It can be either a paper or a digital map.
Nowadays, cartography is done with Geographical Information Systems or G.I.S., which makes a difference between ‘paper’ or ‘digital’ cartography.
A digital cartography, done with G.I.S., is a real tool for forest management, which database can be processed and updated. There are applications for smartphone and digital tablet.
A G.I.S. links data to a geographical position. It is thus possible to locate a plot by town, by estate, by tree variety, by age, etc.
The work of the mapmaker has been improving over these last years, with the use of photographs from planes, of GPS and drones (orthophoto).
II - How is a Forest cartography carried out?
A forest cartography is a database based imperatively on cadastral matrix, notarised certificate(s), mortgage status.
This base is then completed on different levels by the G.I.S.:
A - Administrative and fiscal data :
This data is the ‘identity card’ of the cadastral plot.
It gives information on :
- The legal entities (undivided estate, split ownership, forestry group, companies…)
- The cadastral references (town, hamlet, section, number, subdivision, surface, tax exemption, cadastral income)
- The management documents (SMP, CGPS, CMR)1
- The certifications (PEFC, FSC)
- The fiscal obligation (grants, DEFI, Monichon certificate, IFI – tax on property asset – certificate)
- The VAT system (flat fee or liability)
- The SIRET Numbers (Système informatique pour le Répertoire des Entreprises sur le Territoire)
- The insurance for the forest and the civil liability insurance
B - The technical data :
This data is the ‘identity card’ of the forest plot.
It gives information on :
- The forest (species, structure, composition, etc)
- The origin of the forest (natural or man-made)
- The state of the forest and how it is managed (even-aged or uneven-aged stands, simple coppice, etc)
- The age of the trees
- The stations (dry, moist, mesophilic flora, etc)
- The layout of the plot (rugged, flat, etc)
- The environment (lagoon, marsh, riparian forest, etc)
- The sanitary state of the forest
- The plants (heather, gorses, ferns, moor grass, etc)
- The different kinds of soil (sand, clay, slit, etc)
- The trees mensuration (circumference, height, density, etc)
- The works schedule (cleaning, reforestation, wood management)
C - The geographical data :
It gives information on :
- The cadastral data
- The map – scale 1/25000
- Shows photographs from plane
- The environmental zones (NATURA 2000, registered site, listed site, historic monuments)
- The infrastructures (roads, tracks, paths, ditches, bridges, storage of wood, ‘palombières’, etc)
- The dangers (wells, steep slopes, gas lines, electric lines, various networks, pipes, etc)
D - The works data :
It gives information on :
- The management works (plots, place of storage, transportation track)
- The type of management (clear cut, thinning, fuel-wood, stumps valorisation, etc)
- The forestry works (plot, access)
- The types of forestry work (managements, reforestation, works by power shovel, etc)
- The plot inventory mensuration
All of this data is gathered in a digital database which creates a forest cartography, thanks to a software programme.
III - Why create a forest cartography?
A cartography gives the possibility to gather, via the G.I.S. System, all the data about a forestry estate, such as administrative, fiscal, technical, geographical and works data.
Thanks to the cartography, it is possible to answer all administrative requests, such as:
- Management documents,
- Monichon, IFI, PEFC, FSC Certifications,
- Forest insurances.
Thus, it becomes a much-needed tool for a good forest management:
- A 360° vision of the estate in order to take the right decisions,
- Updated data,
- Updated value (inheritance/gift estimation),
- Dividing up by age, species,
- Location of the wood,
- Location on site,
- Organisation of the wood management work,
- Organisation of the forestry work.
IV - Why carry out a cartography with PLANFOR?
- PLANFOR is supported by an I.T. Department, an administrative manager, forest technicians, drone pilots (orthophoto) and Professional Forest Managers.
- PLANFOR works with a lasting, upgradeable and shared universal database.
- PLANFOR carries out the cartography of a forest estate which relies on real information, such as dendrometric measurements, soil analysis and orthophotos.
- PLANFOR works with a free and universal Q.G.I.S.
- PLANFOR gives free access to updated cartography data online: WEBMAPPING (unlimited, subscription-free access, possibility to download the data on Excel tables).
- PLANFOR is equipped with DRONES to improve the technical diagnosis of the plots.
In addition to the forest cartography, PLANFOR is also able to assist the forest owners for: the forest management, all the forest works, wood selling.
1 SMP = Simple Management Plan (PSG – Plan Simple de Gestion) / CGPS = Code of Good Practice for Sylviculture (CBPS – Code des Bonnes Pratiques Sylvicoles) / CMR = Classic Management Regulations (RTG – Règlement Type de Gestion)
Related Categories: Forest mapping
Your reviews about: Forest mapping |


























































































































































































































































