The different types of Truffles
• The history of Black Truffle growing
• The different types of Truffles
• Choosing the right truffle...
• How truffle trees are produced ?
• Choosing your Truffle Tree
• Planting density of truffle trees
• Soil preparation to Creating a Truffle Plantation
• Planting Truffle Trees
• Maintaining a truffle plantation
• Harvesting the truffle


There are more than a hundred types of mycorrhizae that belong to the Tuber genus. These fungi need to develop in association with a tree’s roots. This is known as symbiosis and is where each party benefits from its association with the other.
In Europe, there are six main varieties that are considered good to eat.
The most appreciated and widespread are the Tuber melanosporum (Périgord truffle) and the Tuber uncinatum (Bourgogne truffle). You can also find the Tuber magnatum (Italian truffle), Tuber brumale (musky truffle), Tuber æstivum (summer truffle) and the Tuber mesentericum (Lorraine truffle).
If you live in a area with good soil but no history of truffle growing, the first thing to decide on is the type of truffle that you want to grow The type of soil that you have and the prevailing climate are two most important factors.

Tuber uncinatum – Bourgogne Truffle
The Bourgogne truffle is noted for its rich fine woody aroma, it has a nutty taste, and these are the qualities that have made its reputation.
The main characteristics of the truffle are its black skin (peridium) and chocolate colored flesh (gleba) The flesh is covered throughout by a network of very fine and closely packed white veins which are reminiscent of a tree’s branches.
It is naturally found in the east of France from Bourgogne up to Alsace, but it could easily be grown in the Atlantic or Mediterranean regions.
It is normally harvested from mid September through to February, as long as there are no harsh frosts.

Tuber melanosporum – Périgord truffle
The Périgord truffle has a very strong aroma and a much-appreciated taste. Its outside is blackish with hints of reddishness or rust. Its flesh is a scarlet brown turning to black on maturity. It is filled with a dense network of fine white veins that branch out.
It is harvested from the beginning of December through to the end of March.
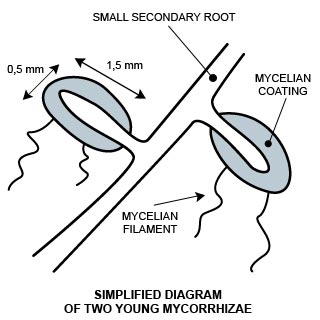
A little biology lesson...
Everything begins with a fungus, the mycelium. This is made up of very fine filaments, which grow thanks to the roots of the tree with which it has a symbiotic relationship. It is normally trees like the oak, hazel, hornbeam or lime. From this symbiotic relationship are born the mycorrhizae, which are part tree and part fungus. It is the filaments from the mycorrhizae that will group together to form the truffles that are so appreciated by the gourmets amongst us.
The spores from the truffles will in turn germinate and create new mycelium, which in their turn will create new mycorrhizae and in the following year new truffles.

How to cook Truffles ?
Even if the truffle incites curiosity amongst many of us, we are often at a loss what to do with it once we have this precious object in front of us…How can we really get the most from this valued black diamond ?
The truffle is best cooked simply, only about 8 to 10 grams per person of this marvelous thing are needed to delight the taste buds of your guests. A dish cannot consist of just the truffle. The truffle should be us as a condiment to bring out its fine and aromatic flavor.
The truffle is eaten raw or very slightly cooked. Cooking can destroy its powerful aromas. Always add it at the last minute to your dishes.
Shavings of the truffle can be infused in cream, béchamel sauce... for about an hour to accompany meat, foie gras or fresh pasta...
Nevertheless, without a doubt the best is the truffle omelette. The day before put the truffle along with the eggs in to an airtight container and place it in the fridge. As the eggshell is porous, it will allow the truffle flavors and aromas to be absorbed by the eggs. When you are ready, slice the truffle finely and mix it in with the beaten eggs. Keep a few slices aside for decoration... Bon appétit !












































































































































































































































